Wireless for Enterprise & Office
802.11n: Longer-Range, Faster-Throughput, Multimedia-Grade Wi-Fi® Networks
The IEEE 802.11n specification is now stable and it has introduced substantial enhancements in Wireless Local-Area Network (WLAN) performance, efficiency and robustness of the 802.11 physical and medium access control layers. The 802.11n products currently on the market demonstrate a significantly higher throughput and improved range. The 802.11n standard promises to achieve as much as 5x the throughput and up to double the range over legacy 802.11 a/b/g technology
At this level of throughput and range performance, 802.11n can support multimedia applications, with the ability to transport multiple high-definition (HD) video streams, while at the same time accommodating Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) streams and data transfers for multiple users with high Quality of Service (QoS) and latest generation security protections in place. In enterprise, campus and municipal networks, 802.11n offers the robustness, throughput, security and QoS capabilities that IT managers have come to expect from wired Ethernet networks.
The developing IEEE 802.11n standard is based on MIMO (multiple-input multiple-output) air interface technology. MIMO is a significant innovation and a technology that is being adapted for use by several non-802.11 wireless data communications standards, including 4G cellular. MIMO employs a technique called spatial multiplexing to transport two or more data streams simultaneously in the same frequency channel. Spatial multiplexing is central to 802.11n and has the potential of doubling the throughput of a wireless channel when two spatial streams are transmitted. Generating multiple spatial streams requires multiple transmitters, multiple receivers and distinct, uncorrelated paths for each stream through the medium. Multiple paths can be achieved using antenna polarization or multipath in the channel.
While the legacy networks operate in a 20 MHz channel, 802.11n defines the use of 20 and 40 MHz channels with up to 4 spatial streams per channel. The Wi-Fi 802.11n presently confines the use of 40 MHz channels to the 5 GHz band. With 4 spatial streams in a 40 MHz channel the maximum transmission data rate is 600 Mbps.
Analyst forecasts that Wi-Fi chipsets will increase from 250 million in 2008 to about 1.1 billion units in 2012. This considerable rate of growth reflects the fact that 802.11n promotes expansion of Wi-Fi into new market segments and applications in the home and in the enterprise.
Home Environment
With its increased coverage and throughput, 802.11n enables HD video and audio-visual (AV) multimedia applications providing sufficient bandwidth to transport multiple video streams to Wi-Fi enabled set-top boxes or TV sets around the house. 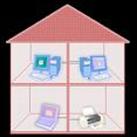 The increased range of 802.11n provides coverage of the entire house, reaching farther than the legacy technology and reducing “dead spots” or low-rate areas in the home.
The increased range of 802.11n provides coverage of the entire house, reaching farther than the legacy technology and reducing “dead spots” or low-rate areas in the home.
Most network transactions, including voice and data services, will benefit significantly from the 802.11n frame aggregation technology. Printing files from PCs to printers, transferring files between PCs and network drives and sharing files between PCs, laptops and other devices on the network becomes more efficient with 802.11n thanks to frame aggregation.
Benefits to enterprises
• Getting rid of the wires, inside and out No LAN & PBX investment any more
• 40%+ saving in TCO of data & voice
• Fast deployment within an hour
• Change floor plan and relocate without re-wiring
802.11n is enterprise-grade technology and will provide IT managers with nearly the same reliable service they have come to expect from their Ethernet networks. Mission-critical enterprise applications, such as Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) access, collaboration tools, voice and video conferencing, will all benefit from the increased throughput and range of 802.11n.
 Also the new efficiencies and enhancements of 802.11n on the MAC and PHY layers, combined with the QoS capabilities, serve to improve the quality of VoIP and to increase the number of simultaneous calls on the air link. Physical layer transmission enhancements of 802.11n, such as Space Time Block Coding (STBC), improve reception even for single receiver Wi-Fi phones by virtue of transmitting multiple copies of a data stream via multiple antennas.
Also the new efficiencies and enhancements of 802.11n on the MAC and PHY layers, combined with the QoS capabilities, serve to improve the quality of VoIP and to increase the number of simultaneous calls on the air link. Physical layer transmission enhancements of 802.11n, such as Space Time Block Coding (STBC), improve reception even for single receiver Wi-Fi phones by virtue of transmitting multiple copies of a data stream via multiple antennas.
Of significant benefit to the Enterprise is lower density of APs, made possible by the improved efficiencies in the MAC, enhancements in the PHY operation and longer reach. Due to faster physical layer transmissions, stations get on and off the air faster, improving the air link efficiency. The MAC layer mechanisms such as block ACK and frame aggregation also improve the air link efficiency by reducing the overhead of packet headers, inter-frame gaps and ACK transmissions.
Legacy stations in the 802.11n network can benefit from better coverage provided by the 802.11n APs’ CSD and MRC techniques and they can also gain increased access to the air link as the new 802.11n devices get on and off the air faster.
Campus and Municipal Networks
• Quick setup
• Only power supply and LAN line are required at premise
• No radio planning, no configuration
• Immediate wireless network available
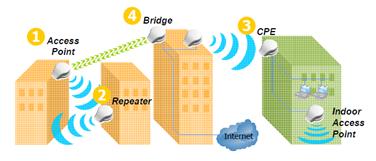 Campus and municipal networks typically operate in challenging environments where range is the biggest issue. 802.11n is well-equipped to improve the operating range even for single-antenna handheld devices used in such outdoors networks. Increased range of handheld devices is achieved through AP transmit and receive diversity mechanisms. Transmit diversity of APs, including STBC and transmit Beam forming, improves the downlink range performance. Receive diversity of APs, including MRC, reciprocate the transmit diversity and thus maintain the range for both the uplink and the downlink directions.
Campus and municipal networks typically operate in challenging environments where range is the biggest issue. 802.11n is well-equipped to improve the operating range even for single-antenna handheld devices used in such outdoors networks. Increased range of handheld devices is achieved through AP transmit and receive diversity mechanisms. Transmit diversity of APs, including STBC and transmit Beam forming, improves the downlink range performance. Receive diversity of APs, including MRC, reciprocate the transmit diversity and thus maintain the range for both the uplink and the downlink directions.
Altai A3 offers the best 802.11n
• Higher speed, larger capacity and larger coverage
• Industrial grade vs. available commercial products in the market
• 250 m large NLOS coverage (3 x 3 MIMO smart antennas)
• 180 Mbps high throughput (IEEE 802.11n multiple radios)
• Support throughput ~10 Mbps/user for 200 users to ~36 Mbps/user for 50 users
• Flexible mounting (wall, ceiling or pole)
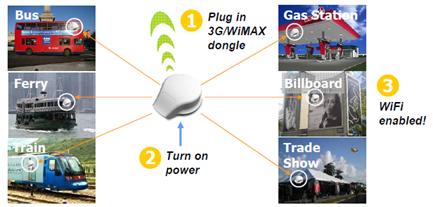 Altai has developed the world´s first IP67 industrial grade 802.11n product with complete water and dust-proof for indoor and outdoor deployments. It supports the latest 3G/WiMAX backhauls and with a simple installation by plugging in 3G/WiMAX dongle the network developer can save man-days.
Altai has developed the world´s first IP67 industrial grade 802.11n product with complete water and dust-proof for indoor and outdoor deployments. It supports the latest 3G/WiMAX backhauls and with a simple installation by plugging in 3G/WiMAX dongle the network developer can save man-days.
All-in-one integrated authentication control and integrated per client, with SSID or AP bandwidth management. It is a turn-key solution for hotspots/ hotzones and other public WiFi services such as parks, buses, hotels, exhibitions and universities.







